How many homes do real estate agents sell a year? That’s a question with a surprisingly varied answer! It depends on a lot of factors, from the agent’s experience and market savvy to the overall health of the economy and even the specific location. We’ll dive into the average number of sales, exploring how things like market segment (luxury versus first-time buyers), geographic location (urban versus rural), and marketing strategies all play a role.
Get ready to uncover the secrets behind a real estate agent’s success!
This exploration will cover key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure success, the impact of economic conditions and marketing, and even how specializing in a niche market can influence sales volume. We’ll also look at future trends and how technology is shaping the industry. By the end, you’ll have a much clearer picture of what a typical year looks like for real estate agents in terms of sales.
Average Number of Home Sales per Agent

Source: site-static.com
Real estate agents’ annual sales vary significantly, influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these variations helps both aspiring and established agents set realistic goals and strategize effectively. This section explores the average number of home sales, considering market segments, geographic location, and agent experience.
Average Sales by Market Segment and Geographic Location
The average number of homes sold annually by a real estate agent differs dramatically depending on the market segment they serve and their geographic location. Luxury real estate agents, for example, typically handle far fewer transactions per year than agents specializing in first-time homebuyers due to the higher price points and longer sales cycles involved in luxury properties. Similarly, agents in densely populated urban areas might sell more homes than those in rural areas with lower population densities and fewer available properties.
While precise figures vary widely based on data source and year, a luxury agent might average 5-15 sales per year, whereas an agent focused on first-time homebuyers could sell 20-40 or more. Urban agents often exceed rural counterparts in sales volume due to higher property turnover.
Factors Influencing Sales Volume
Several key factors influence the number of homes an agent sells annually. Agent experience plays a crucial role; seasoned agents typically possess a larger network of contacts, more refined marketing strategies, and a greater understanding of market dynamics. Effective marketing, including online presence, networking, and client relationship management, directly impacts sales volume. Finally, broader market conditions, such as interest rates, economic growth, and inventory levels, significantly influence the overall number of transactions and, consequently, an individual agent’s sales.
A strong market with high demand and low inventory will naturally lead to higher sales volumes for agents compared to a slower market.
Average Sales by Agent Experience Level
The following table illustrates the estimated average number of home sales per year across different experience levels, considering variations within a specific market segment (e.g., the mid-range market in a moderately sized city). These are averages and should not be taken as absolute figures. Actual results vary widely based on individual skills, market conditions, and other factors.
| Experience Level | Average Sales | Standard Deviation | Market Segment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 1 year | 5-10 | ±5 | Mid-Range |
| 1-5 years | 15-25 | ±8 | Mid-Range |
| 5+ years | 25-40+ | ±12 | Mid-Range |
Factors Affecting Sales Volume: How Many Homes Do Real Estate Agents Sell A Year
Source: jacksonholerealestatesearch.com
Real estate agent sales volume isn’t solely determined by individual effort; it’s a complex interplay of market forces, agent strategies, and brokerage support. Understanding these factors is crucial for both agents aiming to boost their sales and brokers seeking to optimize their team’s performance. This section will delve into the key elements that influence how many homes an agent sells annually.
Economic Conditions and Sales Volume, How many homes do real estate agents sell a year
Broad economic trends significantly impact real estate sales. High interest rates, for example, increase borrowing costs, making mortgages more expensive and reducing buyer demand. This directly translates to fewer sales for agents. Conversely, low interest rates stimulate the market, leading to increased activity and higher sales volumes. Inflation also plays a crucial role; rising prices can decrease affordability, impacting the number of potential buyers, while periods of stable or low inflation generally foster a more active market.
The 2008 financial crisis, characterized by high interest rates and a collapsing housing market, serves as a stark example of how economic downturns dramatically reduce real estate sales. In contrast, the historically low interest rates following the 2008 crisis fueled a period of strong market activity.
Marketing Methods and Sales Success
The effectiveness of an agent’s marketing strategy heavily influences their sales volume. Online listings on platforms like Zillow, Realtor.com, and others are essential for broad reach. A strong online presence, including high-quality photos and detailed property descriptions, can significantly increase visibility and attract potential buyers. Open houses, while requiring more time and effort, provide a valuable opportunity for direct interaction with prospective clients and showcasing properties.
Effective networking, both within the real estate community and with other professionals who might refer clients, is also critical. Consider the difference between an agent who relies solely on online listings versus one who actively participates in community events and cultivates relationships – the latter is likely to see a greater number of sales.
Brokerage Firm Influence on Agent Performance
The brokerage firm an agent works for plays a significant role in their sales success. Larger firms often offer more resources, such as advanced marketing tools, training programs, and administrative support, which can lead to increased sales volume for their agents. Access to a wider network of potential clients and a stronger brand reputation can also be advantageous. However, smaller firms can sometimes foster a more personalized and supportive environment, potentially allowing agents to build stronger client relationships and specialize in niche markets.
The level of commission splits and the support systems provided by the brokerage will also influence the agent’s overall profitability and potentially their motivation to make more sales.
Hierarchical Structure of Factors Influencing Sales Volume
To prioritize the factors affecting sales volume, a hierarchical structure can be beneficial. At the top level is the overall economic climate, encompassing interest rates and inflation. This significantly influences the entire market. The second level would include the agent’s marketing effectiveness and the resources provided by their brokerage firm. These factors directly impact the agent’s ability to generate leads and close deals.
Finally, at the third level are more specific agent-related factors such as negotiation skills, client service, and market knowledge. While all these factors contribute, the broader economic context and the support provided by the brokerage firm tend to have the most significant impact on overall sales volume.
Sales Performance Metrics
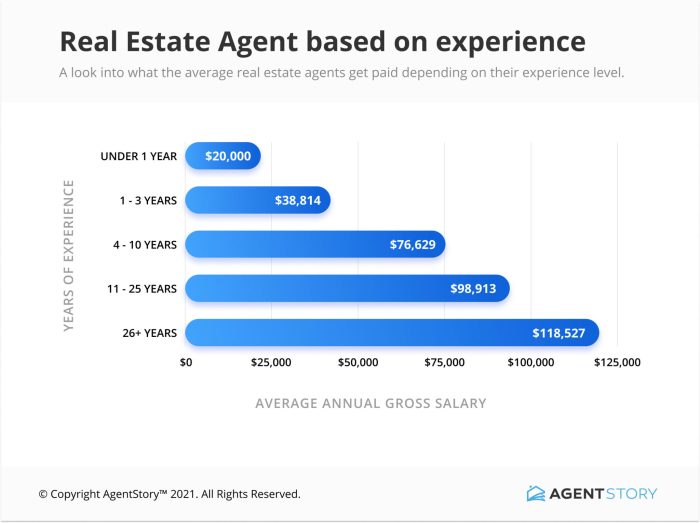
Source: agentstory.com
Understanding how well a real estate agent performs isn’t just about the total number of homes sold. A deeper dive into key performance indicators (KPIs) provides a more nuanced and accurate picture of their productivity and effectiveness. These metrics offer valuable insights for agents seeking self-improvement and for brokerage firms evaluating agent performance.
Several key performance indicators are crucial for measuring real estate agent productivity. These metrics, when analyzed together, paint a comprehensive picture of an agent’s success, allowing for informed decisions regarding strategy and resource allocation.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Real Estate
Several metrics are commonly used to assess a real estate agent’s performance. These KPIs provide a multi-faceted view of their success, moving beyond simply the number of closed deals.
- Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of leads that convert into closed deals. It’s calculated as (Number of Closed Deals / Number of Leads) x 100%. A high conversion rate suggests effective lead nurturing and sales skills. For example, an agent with 10 closed deals out of 50 leads has a 20% conversion rate.
- Average Sales Price: This represents the average price of homes sold by the agent. It’s calculated by dividing the total sales value by the number of closed deals. A higher average sales price indicates the agent is successfully targeting higher-value properties or skillfully negotiating better deals.
- Average Days on Market (DOM): This KPI measures the average number of days a property listed by the agent stays on the market before selling. A lower DOM suggests effective marketing and pricing strategies. It’s calculated by summing the days on market for each sold property and dividing by the number of closed deals.
- Client Satisfaction Score (CSAT): This measures client happiness through surveys or feedback. A high CSAT score reflects strong client relationships and positive experiences. It’s often represented as a percentage of positive feedback.
- Leads Generated: This KPI tracks the number of potential clients the agent acquires through various marketing channels. A higher number of leads often indicates a more proactive and effective marketing strategy.
Visual Representation of Agent Experience and Sales Performance
The following describes a bar chart illustrating the relationship between agent experience (measured in years) and average sales price. This is just one example; other KPIs could be similarly visualized.
The chart’s horizontal axis represents agent experience (in years), ranging from 1 to 10 years. The vertical axis represents the average sales price of homes sold (in thousands of dollars). Data points would be plotted for each experience level, showing the average sales price achieved by agents with that level of experience. For instance, a data point might show that agents with 5 years of experience achieve an average sales price of $500,000, while those with 10 years achieve an average of $750,000.
The chart would visually demonstrate the potential correlation between experience and higher average sales prices, although it’s important to note correlation does not equal causation. Other factors, such as market conditions and agent skill, also play a significant role.
Pitfalls in Interpreting Sales Data and Mitigation Strategies
Misinterpreting sales data can lead to flawed conclusions and ineffective strategies. Several common pitfalls need to be considered.
- Ignoring Market Conditions: A seemingly low sales volume might be due to a slow market, not necessarily poor agent performance. Analyzing sales data in conjunction with broader market trends is crucial.
- Focusing on Single KPIs: Relying solely on one metric (e.g., number of closed deals) provides an incomplete picture. A holistic view encompassing multiple KPIs is essential.
- Lack of Contextual Data: Sales data should be analyzed considering factors like market segment, property type, and geographic location. Comparing apples to oranges (e.g., comparing an agent specializing in luxury homes to one focusing on starter homes) is misleading.
- Ignoring Qualitative Data: Client feedback and testimonials offer valuable qualitative insights that complement quantitative data. A high number of closed deals doesn’t necessarily equate to high client satisfaction.
To avoid these pitfalls, agents and brokerages should utilize data visualization tools, compare performance against market benchmarks, consider external factors influencing sales, and incorporate both quantitative and qualitative data in their analysis.
Agent Specialization and Sales

Source: co.uk
Real estate agents often find success by focusing their efforts on a specific market segment. Specialization allows agents to develop deep expertise, build strong networks, and ultimately, increase their sales volume. However, it’s crucial to understand the trade-offs involved before committing to a niche.
Average Sales Volume by Property Type
The average number of homes sold annually varies significantly depending on the type of property an agent specializes in. Agents focusing on residential properties, particularly in a mid-range market, might sell a higher volume of homes compared to luxury or commercial real estate agents. Luxury real estate, while potentially yielding higher commission per sale, typically involves fewer transactions due to the limited pool of buyers and the longer sales cycles.
Commercial real estate agents often handle fewer, but more complex, deals, resulting in a lower number of sales per year but potentially higher overall revenue. Precise figures are difficult to pin down due to variations in market conditions and agent performance, but it’s safe to say that volume significantly differs across these specializations. For example, a residential agent might average 20-30 sales a year, while a luxury agent might average 5-10, and a commercial agent perhaps 2-5.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Niche Specialization
Specializing in a niche market offers distinct advantages. Developing expertise in a specific area allows agents to become highly sought-after by clients seeking their unique knowledge and experience. This specialization often leads to increased credibility and trust, attracting referrals and repeat business. Building a strong network within a niche also streamlines the sales process, providing access to potential buyers and sellers.
However, specializing also carries risks. Niche markets can be volatile and susceptible to economic downturns, potentially impacting sales volume. Furthermore, limiting oneself to a specific niche might restrict potential earnings if that market experiences a decline. Over-specialization can also lead to missed opportunities in other profitable sectors.
Influence of Specialization on Marketing and Client Acquisition
Agent specialization profoundly impacts marketing strategies and client acquisition. Targeted marketing campaigns become more effective when focused on a specific demographic or property type. For instance, a luxury real estate agent might utilize high-end publications and exclusive events to reach potential clients, whereas a residential agent might focus on online portals and community engagement. Client acquisition strategies also adapt to the chosen niche.
Building relationships with local businesses, attending relevant industry events, and networking within the specialized community are crucial for success. Effective branding and messaging, highlighting the agent’s unique expertise and understanding of the specific market, are vital for attracting the right clientele.
Developing a Successful Niche Specialization Strategy
Developing a successful niche specialization strategy requires careful planning and execution. Here are key steps:
- Identify your passion and skills: Choose a niche that genuinely interests you and aligns with your existing skills and experience. This passion will fuel your commitment and drive your success.
- Conduct thorough market research: Analyze the demand, competition, and potential profitability of your chosen niche. Understanding the market dynamics is essential for informed decision-making.
- Develop a targeted marketing plan: Craft a marketing strategy specifically designed to reach your target audience within your chosen niche. This includes selecting appropriate channels and messaging.
- Build strong relationships: Network extensively within your chosen niche, building relationships with potential clients, referral sources, and other industry professionals.
- Continuously learn and adapt: Stay updated on market trends, legal requirements, and best practices within your niche. Continuous learning is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Track your results and refine your strategy: Regularly monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your strategy based on your performance and market feedback.
Future Trends and Projections

Source: realestatelicensewizard.com
The real estate market is dynamic, constantly evolving due to technological advancements, shifting demographics, and economic fluctuations. Predicting the future is inherently uncertain, but by analyzing current trends, we can make informed projections about how these factors will influence the number of homes sold per real estate agent in the coming years.The intersection of technology and real estate is reshaping the industry at a rapid pace, impacting agent productivity and sales volume significantly.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Technological innovations are streamlining processes and enhancing the agent-client experience. Virtual tours, for instance, allow potential buyers to explore properties remotely, saving time and effort for both parties. This increases the number of properties an agent can effectively showcase. AI-powered tools, such as automated valuation models (AVMs) and lead generation software, are improving efficiency by automating tasks like property appraisal and marketing.
For example, a platform like Zillow uses AVM to provide estimated home values, freeing up agents to focus on client interaction and negotiation. The increased efficiency afforded by these tools allows agents to manage a larger portfolio of properties and potentially close more deals. However, agents must adapt and learn to effectively utilize these technologies to remain competitive.
Over-reliance on technology without the human touch can negatively impact the client experience.
Challenges and Opportunities for Real Estate Agents
The coming years present both challenges and exciting opportunities for real estate agents. Increased competition, from both traditional agents and new entrants leveraging technology, will require agents to constantly upgrade their skills and adapt their business models. Maintaining a strong personal brand and building genuine client relationships will be crucial for success. The opportunity lies in specializing in niche markets, offering personalized services, and utilizing technology to enhance efficiency and client experience.
For instance, an agent specializing in sustainable homes could cater to a growing segment of environmentally conscious buyers. This focused approach allows for deeper market knowledge and targeted marketing efforts, potentially leading to higher sales volume.
Demographic Shifts and Their Influence on Sales
Demographic trends significantly influence the real estate market. For example, the increasing number of millennials entering the home-buying market will create a surge in demand, especially for properties in urban areas and those offering smart home features. Conversely, an aging population might lead to an increase in demand for retirement communities and properties suitable for older adults. Agents who understand these shifts and tailor their services to specific demographics will be better positioned to succeed.
For example, an agent focusing on the millennial market might leverage social media marketing and highlight features appealing to younger buyers. This targeted approach increases the chances of successful transactions. Conversely, an agent specializing in retirement communities would need to understand the specific needs and preferences of this demographic. Adapting to these shifts will be critical to maintaining and increasing sales volume.
Concluding Remarks

Source: realestateagentpdx.com
So, how many homes
-do* real estate agents sell annually? There’s no single magic number. Success is a blend of experience, market knowledge, effective strategies, and a bit of luck. Understanding the factors influencing sales—from economic trends to personal marketing approaches and specialization—is key to painting a realistic picture. By analyzing various metrics and anticipating future trends, both agents and clients can make more informed decisions in this dynamic market.
Remember, the numbers are just a starting point; the real story lies in the individual effort and market conditions at play.